As we age, our bodies undergo a series of changes, and our bones and joints are no exception. In older adults, orthopedic issues such as joint pain, fractures, and arthritis become more common. These conditions can have a significant impact on the quality of life for seniors, making it difficult for them to perform daily activities and enjoy their golden years.
However, there are many treatment and prevention options available to help older adults manage orthopedic issues and maintain their independence. Finding a good doctor like Orthopedics In LA is crucial to help you treat these conditions.
Arthritis
Arthritis is a term used to describe a group of conditions that cause inflammation in the joints. The most common types of arthritis in older adults are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis is caused by the wear and tear of the joints over time, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation in the joints.
Symptoms of arthritis can include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. As the condition progresses, it can become increasingly difficult to perform daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and grasping objects.
Prevention
While there is no known cure for arthritis, there are several ways to prevent it from developing or worsening. One of the most important things you can do is to maintain a healthy weight. Carrying extra weight puts additional stress on your joints, which can increase your risk of developing arthritis.
Exercise is also essential for maintaining joint health. Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling can help keep your joints flexible and reduce inflammation. Strength training exercises can also help build muscle around the joints, providing additional support.
Treatment
Treatment for arthritis depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, over-the-counter pain medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may be sufficient. However, in more severe cases, prescription medications or injections may be necessary to manage pain and inflammation.
Physical therapy can also be beneficial for those with arthritis. A physical therapist can help you develop a customized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around your joints and improve your flexibility.
Joint Fractures
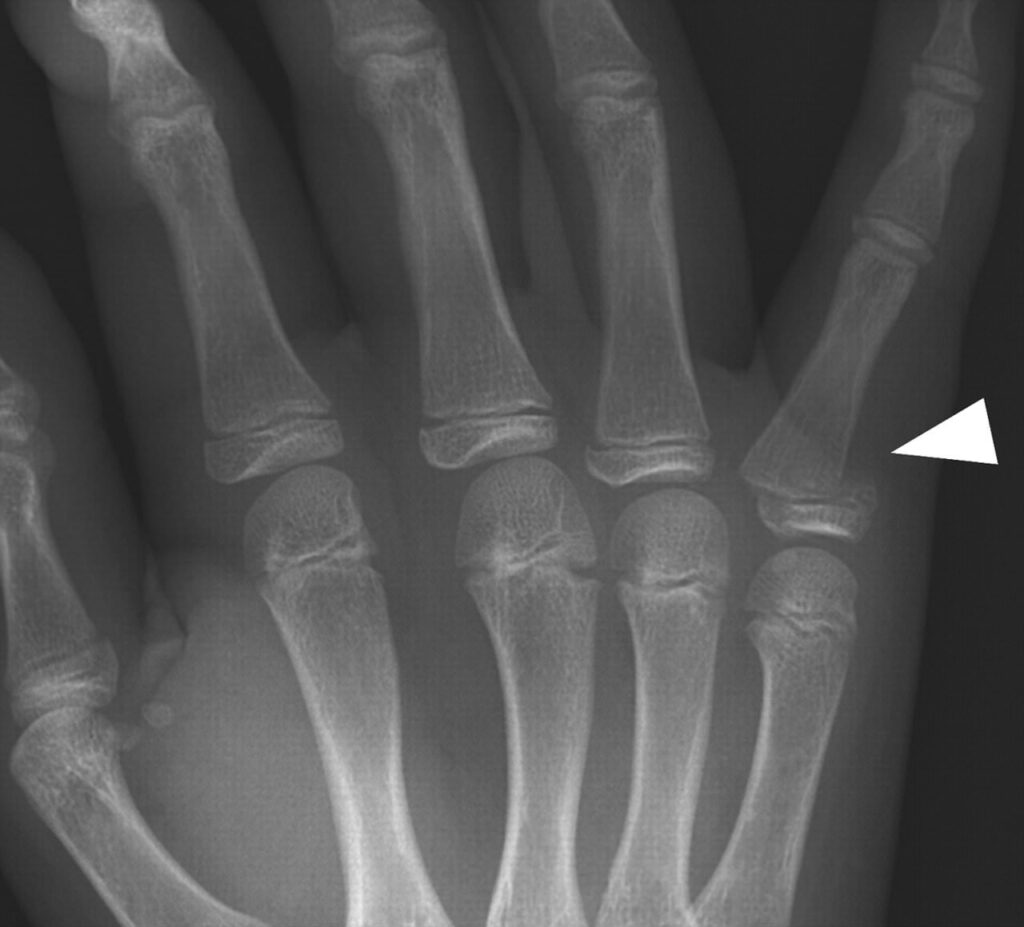
Fractures, or broken bones, are common orthopedic issues in older adults. As we age, our bones become weaker and more brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures. The most common sites for fractures in older adults are the hip, wrist, and spine.
Symptoms of a fracture can include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected limb. In severe cases, the bone may protrude through the skin.
Prevention
One of the best ways to prevent fractures is to maintain strong bones. This can be achieved through a combination of diet and exercise. Foods that are high in calcium, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals, can help keep bones strong. Vitamin D is also important for bone health, as it helps the body absorb calcium.
Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, and dancing can also help strengthen bones. Strength training exercises can help build muscle mass, which can also help protect bones from injury.
Fall prevention is also crucial in preventing fractures. Older adults can reduce their risk of falls by keeping their homes well-lit, removing tripping hazards such as rugs and clutter, and wearing appropriate footwear.
Treatment
The treatment for a fracture depends on the severity of the injury. In some cases, immobilization with a cast or brace may be sufficient. However, in more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to realign the bones and stabilize the fracture.
After a fracture, rehabilitation is essential to help restore mobility and strength. Physical therapy can help improve the range of motion and build muscle around the affected area.
Osteoporosis
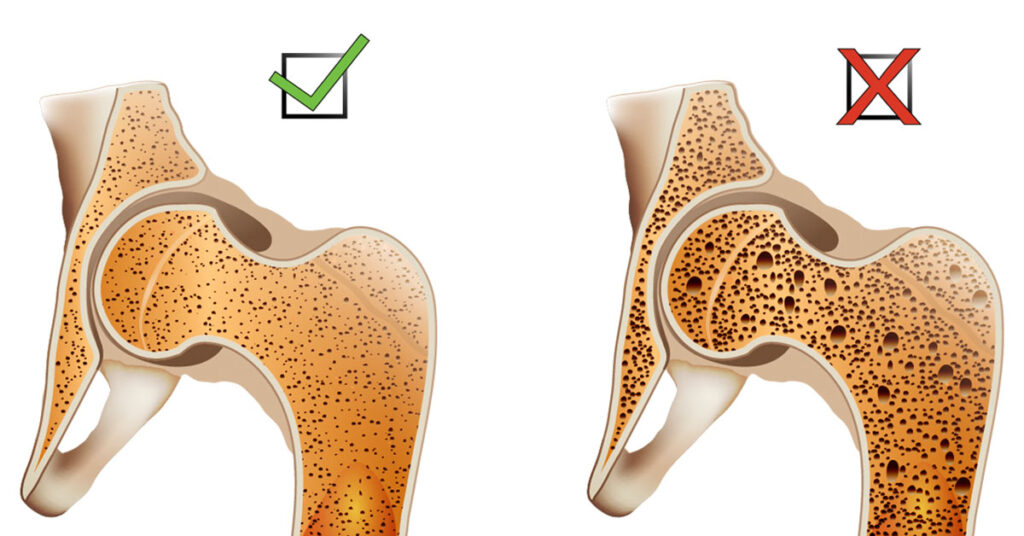
Osteoporosis is a condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures. It is a common condition in older adults, particularly women.
Symptoms of osteoporosis may not be noticeable until a fracture occurs. However, some early signs can include back pain, loss of height, and a stooped posture.
Prevention
To prevent osteoporosis, it’s important to maintain healthy and strong bones, which can be achieved by a combination of a nutritious diet and regular exercise. Consuming foods that are rich in calcium and vitamin D, like dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals, can help maintain strong bones. Engaging in weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, and dancing, as well as strength training exercises, can help strengthen bones and build muscle mass, which can also protect bones from injury.
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also help reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Treatment
Treatment for osteoporosis typically involves medications to increase bone density and reduce the risk of fractures. Bisphosphonates are a common class of medications used to treat osteoporosis. These drugs work by slowing the breakdown of bone and increasing bone density.
Calcitonin and hormone therapy are other medications that may be used to treat osteoporosis. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair fractures or replace damaged joints.
Joint Replacement
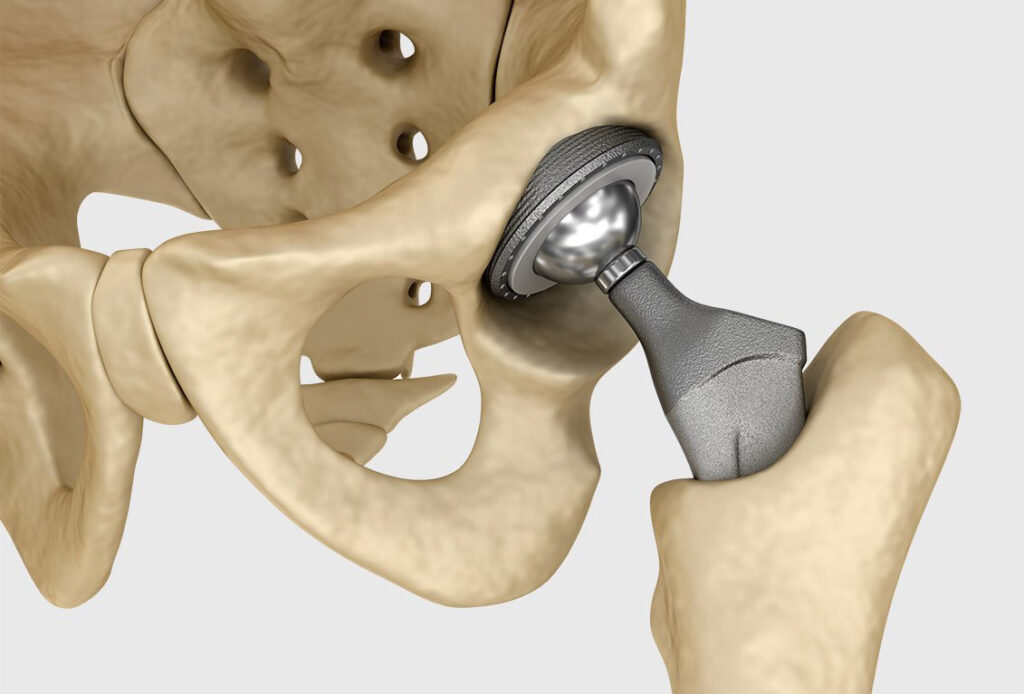
Joint replacement surgery is a common procedure in older adults, particularly for those with severe arthritis or joint damage. The most common joints that are replaced are the hip and knee.
During joint replacement surgery, the damaged joint is removed and replaced with an artificial joint made of metal or plastic. This can help reduce pain and improve mobility.
Prevention
Preventing the need for joint replacement surgery involves maintaining joint health. This can be achieved through a combination of exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding repetitive motions that put stress on the joints.
Treatment
Joint replacement surgery is typically a last resort for those with severe joint damage or arthritis that cannot be managed with other treatments. The procedure can be highly effective in reducing pain and improving mobility.
Rehabilitation after joint replacement surgery is essential to help restore mobility and strength. Physical therapy can help improve the range of motion and build muscle around the affected joint.
Conclusion
Orthopedic issues are a common concern for older adults, but there are many ways to prevent and treat these conditions. Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding falls can all help reduce the risk of fractures and joint damage.
If you are experiencing joint pain or other orthopedic issues, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider. They can help develop a treatment plan that is customized to your individual needs and goals.
With proper care and treatment, older adults can maintain their mobility and independence and enjoy a high quality of life well into their golden years.
